Formality Detection in Text: Model Evaluation through Comparison against Transformer-Based Systems
This project explores the development of a robust system for the evaluation of models trained to evaluate the level of formality of natural language. A full report outlining the methods, results and conclusions can be found here.
As benchmarks of state-of-the-art performance, I used the pre-trained transformer models of Dementieva et al. (2023) available on HuggingFace. Instead of regression, the task is simplified into formal vs. informal categories, benchmarking model performance on a new dataset derived from Pavlick et al.'s formality annotations.
1. Data Preparation & Exploratory Analysis
I adapted the Pavlick Formality Scores dataset (sentences annotated with formality scores from -3 to +3 by humans) into a balanced binary classification set. Ambiguous examples near zero were discarded, and the remaining were thresholded into formal vs. informal.
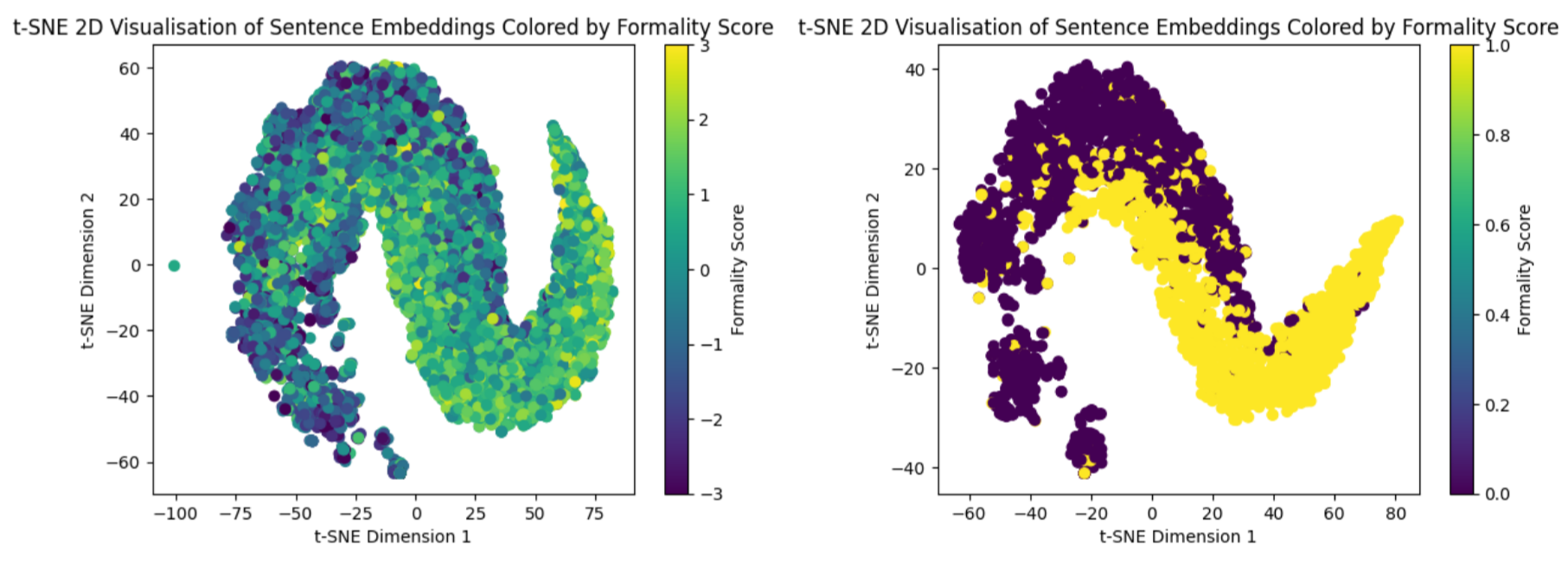
GloVe-25 embeddings were used to vectorise sentences, followed by t-SNE dimensionality reduction. The visualization revealed clear separability between classes, indicating the suitability of a classification approach.
2. Model Selection & Evaluation Metrics
Three transformer-based pre-trained models from Hugging Face were benchmarked:
- XLM-RoBERTa fine-tuned on X-FORMAL (multilingual)
- mDistilBERT fine-tuned on X-FORMAL (multilingual)
- DeBERTa-large fine-tuned on GYAFC (English-only)
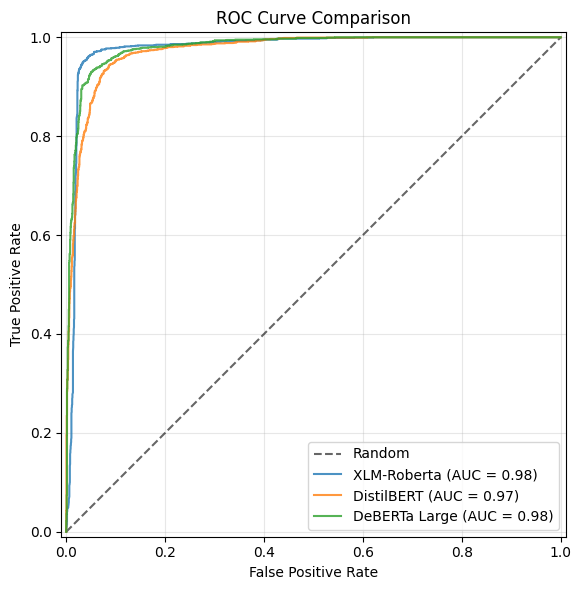
Performance was measured using accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC AUC. The monolingual DeBERTa-large model performed best overall, though all models showed strong recall.
3. Experimental Setup
Evaluations were performed in a Google Colab environment using only the held-out test split, enabling fast iteration. Pre-trained model logits were also recorded for potential future correlation analysis against continuous formality scores.
4. Results & Insights
The DeBERTa-large model achieved the highest scores across metrics, confirming that monolingual models fine-tuned on relevant data generalise effectively to new binary formality tasks. Multilingual models also showed strong performance, suggesting good cross-lingual transfer.
The confusion matrices for the three models are included and discussed in the report linked above.
5. Conclusions & Future Directions
This project confirms that transformer-based models fine-tuned for formality detection perform strongly on new data. The evaluation pipeline developed here is reusable for benchmarking future models. A promising extension would be correlating model logits with continuous formality scores to assess sensitivity to degree of formality.